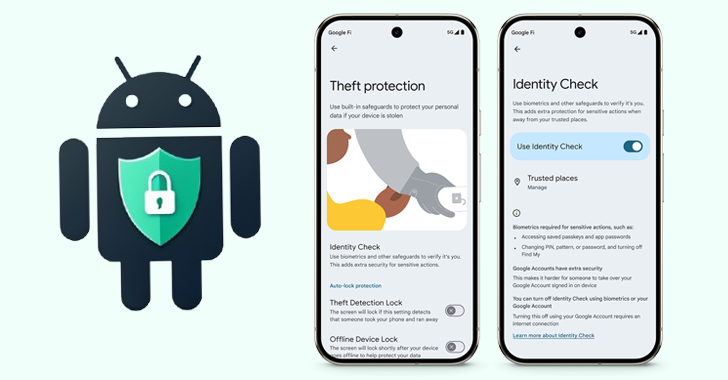
Google has launched a new feature called Verifying personality For supported Android devices, blocking confidential biometric settings when being out of trusted places.
“If you turn on the face check, your device will need obvious biometric authentication to access certain confidential resources if you are out of trusted places,” Google. said in a posting message.
In doing so, biometric authentication will required for the following –
- Enable Saved Passwords and Key using Google Password Manager
- Autovging Passwords in programs with Google Password Manager, except Chrome
- Change screen lock, eg PIN, Template and Password
- Changing biometric data such as a fingerprint or face recognition
- Run the reset to the factory settings
- Turn off “Find my device”.
- Disable all the protection features from theft
- View reliable places
- Disconnect your face check
- Set up a new device with your current device
- Add or delete Google account
- Access to developer parameters
The identification check is also intended to include improved Google Accounts to prevent unauthorized persons from receiving control over any Google account that entered the device.
Currently, the function is limited by Google Pixel’s own phones with Android 15 and the corresponding Samsung Galaxy phones with One UI 7. It can be turned on by going to Settings> Google> All Services> Protection Facial> Checking Person.
Disclosure is happening like Google adding continuous stream of security features protect the devices from theftSuch as blocking the theft, lock, autonomous device and remote lock.
Google also said she has released her blocking of artificial intelligence on all Android 10 and later versions around the world, and that she collaborates with GSMA and industry experts in the fight against mobile devices by sharing information, tools and Prevention. Techniques.
Development also follows him start Chrome online stores for enterprises that allow organizations to create a selected expansion list that can be installed in the web browser staff, and minimizes the risk of installing potentially harmful or unverified additions to users.
Last month A Phisching Company The Chrome extension developers have been found to have inserted a malicious code for collecting confidential data, such as API keys, Cookie sessions and other authentication markers from websites such as Chatgpt and Facebook for business.
The attack on the supply chain is said to have been active in December 2023, the French Cybersecurity campaign SEKOIA said in a new analysis published this week.
“This threatening specializes in the distribution of malicious Chrome extensions to collect confidential data,” the company said saidcharacterizing the enemy as persistent.
“At the end of November 2024, the attacker changed his way of expanding his own malicious Chrome extensions through fake websites on hacking legal Chrome extensions through phishing sheets, malicious Oauth and malicious code, rooted in hacked Chrome.”