It is estimated that a remote GitHub repository that advertised WordPress’ online content management system (CMS) tool allowed more than 390,000 credentials to be stolen.
The malicious activity is part of a larger attack campaign launched by a threat actor dubbed MUT-1244 (where MUT refers to “Mysterious Unattributed Threat”) by Datadog Security Labs, which includes phishing and several trojanized GitHub repositories that post proof of concept. (PoC) code to exploit known security flaws.
“Victims are believed to be attackers, including pentesters and security researchers, as well as malicious threat actors, and had their sensitive data stolen, such as private SSH keys and AWS access keys,” researcher Christophe Taffani -Dariper, Matt Muir and Adrian Korn said in an analysis shared with The Hacker News.
Not surprisingly, security researchers have been an attractive target, including for threat actors nation-state groups from North Koreaas compromising their systems can provide information about possible exploits related to undisclosed security flaws that they can work on, which can then be used to launch further attacks.
In recent years there is arose trend where attackers to try write with a capital letter about exposing vulnerabilities to create GitHub repositories using fake profiles that claim to post PoCs for the flaws, but are actually created to steal data and even demand payment in exchange for the exploit.
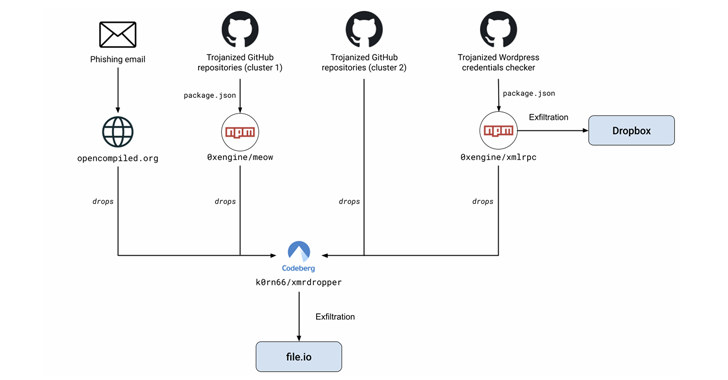
Campaigns conducted by MUT-1244 include not only the use of trojanized GitHub repositories, but also phishing emails that act as a conduit to deliver a second-stage payload capable of dumping a cryptocurrency miner, as well as stealing system information, private SSH keys, environment variables and content associated with specific folders (such as ~/.aws) in File.io.
One such repository was “github(.)com/hpc20235/yawpp” claiming to be “Another WordPress Poster”. Before GitHub was removed, it contained two scripts, one for validating WordPress credentials and one for creating posts using XML-RPC API.
But the tool also contained malicious code in the form of a fake npm dependency, a package called @0xengine/xmlrpc who deployed the same malware. It was originally published on npm in October 2023 as a JavaScript-based XML-RPC server and client for Node.js. The library is no longer available for download.
Notably, cybersecurity company Checkmarx revealed last month that the npm package had remained active for more than a year, attracting around 1,790 downloads.
The yawpp GitHub project is said to have allowed over 390,000 credentials, likely for WordPress accounts, to be stolen into an attacker-controlled Dropbox account by compromising unrelated threat actors who had access to those credentials from using illegal means.
Another method used to deliver the payload involves sending phishing emails to researchers, tricking them into clicking on links that tell them to launch a terminal and copy and paste a shell command to perform the supposed kernel update. Discovery means the first time a Click Fix-style an attack has been documented against Linux systems.
“The second initial access vector that MUT-1244 uses is a set of malicious GitHub users who publish fake proofs of concepts for CVEs,” the researchers explained. “Most of them were created in October or November (2024), have no legitimate business and have an AI-generated profile picture.”
Some of these fake PoC repositories were highlighted earlier Alex Kaganovich, Global Head of Offensive Security at Colgate-Palmolive, in mid-October 2024. But the interesting twist is that the second-stage malware spreads in four different ways –
- Backdoored configuration file compilation
- A malicious payload embedded in a PDF file
- Using the Python dropper
- Enabling the malicious npm package “0xengine/meow”
“MUT-1244 was able to compromise the system of dozens of victims, mostly Red Commanders, security researchers, and anyone interested in downloading the PoC exploit code,” the researchers said. “This allowed MUT-1244 to access sensitive information, including private SSH keys, AWS credentials, and command history.”