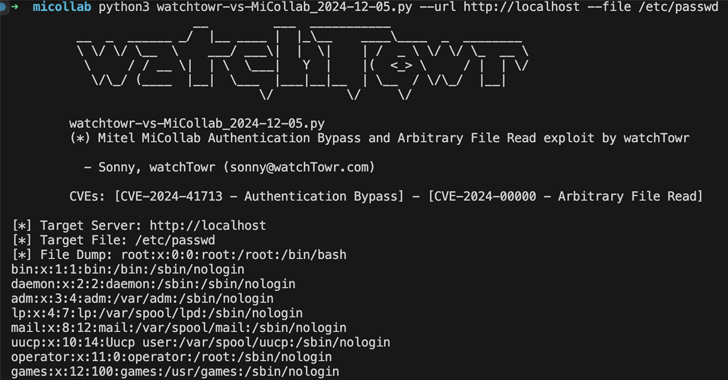
Cyber security researchers have released a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit that combines a patched critical security flaw affecting Mitel MiCollab with arbitrary zero-day file reading, allowing an attacker to access files from susceptible instances.
The critical vulnerability in question is CVE-2024-41713 (CVSS Score: 9.8), which relates to insufficient input validation in Mitel MiCollab’s NuPoint Unified Messaging (NPM) component, leading to an attack bypassing the path.
MiCollab is a software and hardware solution which integrates chat, voice, video and SMS messaging with Microsoft Teams and other apps. NPM is a voice mail server systemwhich allows users to access their voice messages in a variety of ways, including remotely or through the Microsoft Outlook client.
WatchTowr Labs, in a the report shared with The Hacker News, said it discovered CVE-2024-41713 as part of its efforts to reproduce CVE-2024-35286 (CVSS Score: 9.8), another critical flaw in the NPM component that could allow an attacker to gain access to sensitive information and perform arbitrary database and management operations.
The SQL implementation bug was fixed by Mitel in late May 2024 with the release of MiCollab version 9.8 SP1 (9.8.1.5).
What makes the new vulnerability notable is what it includes passing input “..;/” in an HTTP request to the ReconcileWizard component to plant an attacker in the root of the application server, making it possible to access sensitive information (such as /etc/passwd) without authentication.
WatchTowr Labs’ analysis further revealed that the authentication bypass may be related to an unpatched flaw in reading an arbitrary file after authentication to extract sensitive information.
“Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could allow an attacker to gain unauthorized access, potentially impacting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system,” Mittel said. said in the advisory for CVE-2024-41713.
“If the vulnerability is successfully exploited, an attacker could gain unauthenticated access to staging information, including non-sensitive user and network information, and perform unauthorized administrative actions on the MiCollab server.”
After responsible disclosure, CVE-2024-41713 was included in MiCollab version 9.8 SP2 (9.8.2.12) or later as of October 9, 2024.
“On a more technical level, this investigation has demonstrated several valuable lessons,” said security researcher Sonny MacDonald.
“First, it served as a real-world example that full access to the source code is not always necessary – even when studying vulnerabilities to reproduce a known weakness of a COTS solution. Depending on the depth of the CVE description, some good web searching skills can be the basis for successful vulnerability hunting.”
It should be noted that MiCollab 9.8 SP2 (9.8.2.12) also addresses a separate SQL injection vulnerability in the Audio, Web, and Video Conferencing (AWV) component (CVE-2024-47223CVSS score: 9.4) that can have serious consequences ranging from information disclosure to making arbitrary database queries that can cause system inoperability.
The disclosure comes after Rapid7 detailed several security flaws in the Lorex 2K Indoor Wi-Fi Security Camera (CVE-2024-52544 through CVE-2024-52548) that can be combined to achieve remote code execution ( RCE).
In a hypothetical attack scenario, the first three vulnerabilities could be used to reset the target device’s administrator password to one of the adversary’s choices, using access to view live video and audio feeds from the device, or using the remaining two flaws to achieve an elevated RCE.
“The exploit chain consists of five different vulnerabilities that work together in two stages to achieve an unauthenticated RCE,” – Security researcher Stephen Feuer noted.
“Phase 1 performs an authentication bypass, allowing a remote, unauthenticated attacker to reset the device’s administrator password to a password of the attacker’s choice. Phase 2 provides remote code execution by using the authentication bypass in Phase 1 to perform an authenticated stack-based buffer overflow. and execute an operating system (OS) command with root privileges.”