Cybersecurity researchers have discovered nearly two dozen security flaws in 15 different machine learning (ML) open source projects.
These include both server-side and client-side vulnerabilities, software supply chain security firm JFrog said in an analysis published last week.
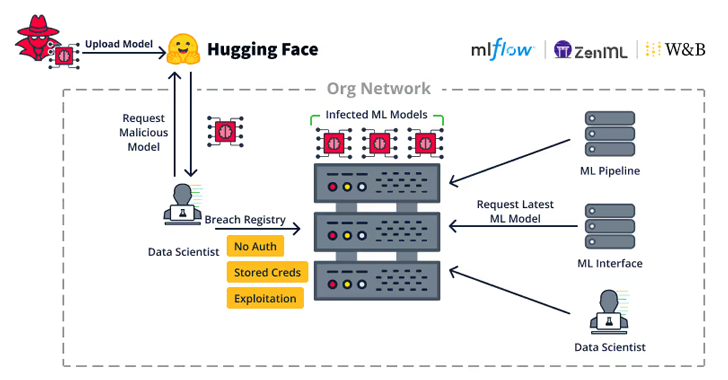
Server-side vulnerabilities “allow attackers to hijack critical servers in an organization, such as ML model registries, ML databases, and ML pipelines.” said.
The vulnerabilities identified in Weave, ZenML, Deep Lake, Vanna.AI, and Mage AI have been broken down into broader subcategories that allow remote hijacking of model registries, ML database structures, and hijacking of ML pipelines.
A brief description of the identified flaws is given below –
- CVE-2024-7340 (CVSS Score: 8.8) – A directory traversal vulnerability in the Weave ML toolkit that allows files to be read across the entire file system, effectively allowing a low-privileged authenticated user to elevate their privileges to the administrator role by reading a file named “api_keys. ibd” (addressed to version 0.50.8)
- Improper access control vulnerability in ZenML MLOps that allows a user with access to a managed ZenML server to elevate their privileges from observer to full administrator privileges, giving an attacker the ability to modify or read the Secret Store (no CVE ID)
- CVE-2024-6507 (CVSS Score: 8.1) – Command injection vulnerability in Deep Lake’s AI-driven database that allows attackers to inject system commands when loading a remote Kaggle dataset due to lack of proper input sanitization (addressed in version 3.9.11)
- CVE-2024-5565 (CVSS Score: 8.1) – A rapid injection vulnerability in the Vanna.AI library that could is exploited to achieve remote code execution on the underlying host
- CVE-2024-45187 (CVSS Score: 7.1) – Privilege misassignment vulnerability that allows guest users in the Mage AI framework to remotely execute arbitrary code via the Mage AI terminal server due to being assigned elevated privileges and remaining active for a default period of 30 days despite the removal
- CVE-2024-45188, CVE-2024-45189and CVE-2024-45190 (CVSS Score: 6.5) – Multiple path traversal vulnerabilities in Mage AI that allow remote users with the View role to read arbitrary text files from the Mage server via File Content, Git Content, and Pipeline Interaction queries. , respectively
“Because MLOps pipelines can access ML datasets, train ML models, and publish ML models, exploiting an ML pipeline can lead to an extremely serious breach,” JFrog said.
“Each of the attacks mentioned in this blog (ML Model backdoor, ML data poisoning, etc.) can be performed by an attacker depending on the access of the MLOps pipeline to these resources.
Disclosure occurs two months after the campaign uncovered more than 20 vulnerabilities that can be exploited to attack MLOps platforms.
It also follows the release of a codenamed defense structure Praying mantis which uses operational implementation as a way to combat cyberattacks Large Language Models (LLM) with more than 95% efficiency.
“After detecting an automated cyberattack, Mantis carefully processes the input data in the system’s response, forcing the attacker’s LLM to disrupt its own operations (passive defense) or even compromise the attacker’s machine (active defense),” – a group of scientists from George Mason University said.
“By purposefully deploying vulnerable decoy services to attract the attacker and using dynamic fast injections for the attacker’s LLM, Mantis can autonomously hack the attacker.”