A government organization and a religious organization in Taiwan have been targeted by a China-linked threat known as The elusive panda which infected them with a previously undocumented post-compromise toolkit codenamed CloudScout.
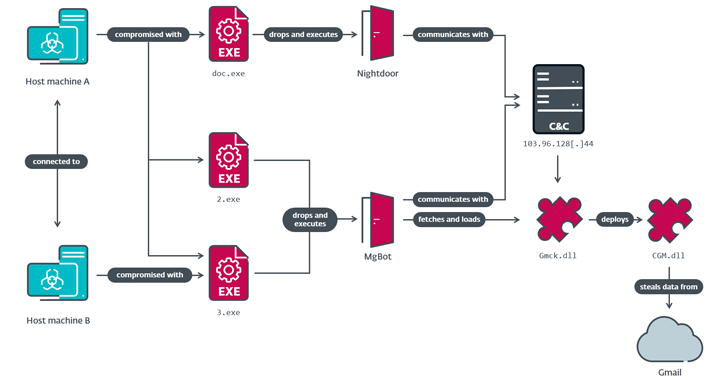
“The CloudScout toolkit is capable of extracting data from various cloud services using stolen web session cookies,” ESET security researcher An Ho said. “Through the CloudScout plug-in, it works seamlessly with MgBot, Evasive Panda’s proprietary malware framework.”
A Slovak cybersecurity company used .NET-based malware that was discovered between May 2022 and February 2023. It includes 10 different modules written in C#, three of which are designed to steal data from Google Drive, Gmail and Outlook. The purpose of the remaining modules remains unknown.
Evasive Panda, also tracked as Bronze Highland, Daggerfly and StormBamboo, appears cyber espionage group which has a track record of strikes at various organizations in Taiwan and Hong Kong. He is also known for orchestrating attacks on watering holes and supply chains targeting the Tibetan diaspora.
What sets the threat actor apart from the rest is the use of multiple initial access vectors, ranging from newly discovered security flaws to hacking the supply chain by poisoning DNS, hacking victim networks, and deploying MgBot and Nightdoor.
ESET said the CloudScout modules are designed to hijack authenticated web browser sessions by stealing cookies and using them to gain unauthorized access to Google Drive, Gmail and Outlook. Each of these modules is deployed using the MgBot plugin, programmed in C++.
“At the heart of CloudScout is the CommonUtilities package, which provides all the necessary low-level libraries for the modules to work,” Ho explained.
“CommonUtilities contains quite a few custom-implemented libraries, despite the large availability of similar open-source libraries on the Internet. These custom libraries give developers more flexibility and control over the inner workings of their implant compared to open source alternatives.”
This includes –
- HTTPAccess, which provides functions for handling HTTP communication
- ManagedCookie, which provides functionality to manage cookies for web requests between CloudScout and the target service
- Lumberjack
- SimpleJSON
The information collected by the three modules—mail folder lists, email messages (including attachments), and files with specific extensions (.doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .ppt, .pptx, .pdf, and .txt)—is compressed into ZIP archive for subsequent exfiltration by either MgBot or Nightdoor.
However, new security mechanisms introduced by Google, such as device-linked session credentials (DBSK) and App-bound encryption sure to make the cookie-stealing malware obsolete.
“CloudScout is a .NET toolkit that Evasive Panda uses to steal data stored in cloud services,” Ho said. “It is implemented as an extension to MgBot and uses a cookie transfer technique to intercept authenticated sessions from web browsers.”
The development comes after the Canadian government accused a “sophisticated state-sponsored threat actor” from China of conducting extensive intelligence operations over several months against multiple domains in Canada.
“The majority of affected organizations were Government of Canada departments and agencies, as well as federal political parties, the House of Commons and the Senate,” it said. said in the statement.
“They also targeted dozens of organizations, including democratic institutions, critical infrastructure, the defense sector, media organizations, think tanks and non-governmental organizations.”