A threat actor known as The mysterious elephant observed the use of an advanced version of the malware called Asynshell.
The attack campaign is said to have used Hajj-themed decoys to trick victims into executing a malicious payload disguised as a Microsoft Compiled HTML Help (CHM) file, Knownsec 404 command said in an analysis published today.
Mysterious Elephant, which is also known as APT-K-47, is a threat actor of South Asian origin that has been active since at least 2022, primarily against Pakistani organizations.
The group’s tactics and tools were found to share similarities with those of other threat actors operating in the region, such as SideWinder, Confucius, and Bitter.
In October 2023, the group was connected to a phishing campaign that deployed a backdoor called ORPCBackdoor as part of attacks targeting Pakistan and other countries.
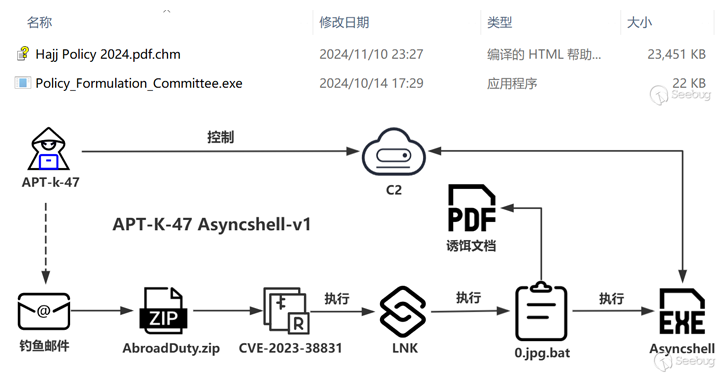
The exact initial access vector used by Mysterious Elephant in the latest campaign is unknown, but it likely involved the use of phishing emails. The method leads to the delivery of a ZIP archive containing two files: a CHM file that claims to be about the 2024 Hajj policy, and a hidden executable.
When CHM starts, it is used to display the decoy document, a legal pdf file hosted on the website of the Government of Pakistan for Religious Affairs and Interfaith Harmony, while the binary executes inconspicuously in the background.
A relatively simple malware designed to install a shell cmd with a remote server, with the Knownsec 404 identifying functional matches with Asyncshell, another tool the threat has repeatedly used since mid-2023.
To date, four different versions of Asyncshell have been discovered that boast cmd and PowerShell command execution capabilities. The initial attack chains that spread the malware were found to exploit a security flaw in WinRAR (CVE-2023-38831CVSS score: 7.8) to cause infection.
Additionally, subsequent iterations of the malware have moved from using TCP to HTTPS for command-and-control (C2) communication, not to mention using an updated attack sequence that uses a Visual Basic script to display a decoy document and launch its scheduled job tool.
“APT-K-47 is seen to frequently use Asyncshell to launch its attack since 2023 and has gradually upgraded its attack chain and payload code,” the Knownsec 404 team said.
“In recent attacks, this group cleverly used masked service requests to control the final address of the shell server, changing the fixed C2 of previous versions to a variable C2, which shows the importance of APT-k-47’s internal organization locations in Asyncshell. “