Malware known as GootLoader continues to be actively used by threat actors looking to deliver additional payloads to compromised nodes.
“Updates to the GootLoader payload have resulted in multiple versions of GootLoader, with GootLoader 3 currently in active use,” according to cybersecurity firm Cybereason. said in an analysis published last week.
“While some details of GootLoader payloads have changed over time, infection strategies and general functionality remain similar to the malware’s resurgence in 2020.”
GootLoader, a malware downloader part of Art Gootkit a banking trojan associated with a threat called Hive0127 (aka UNC2565). It abuses JavaScript to load post-exploitation tools and spreads using search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning tactics.
It usually serves as a delivery conduit for various payloads such as Cobalt Strike, Gootkit, IcedID, Kronos, REvil, and SystemBC.
In recent months, the threat actors behind GootLoader have also released their own command and control tool (C2) and a lateral movement tool called GootBotindicating that “the group is expanding its market to gain a wider audience for its financial gains.”
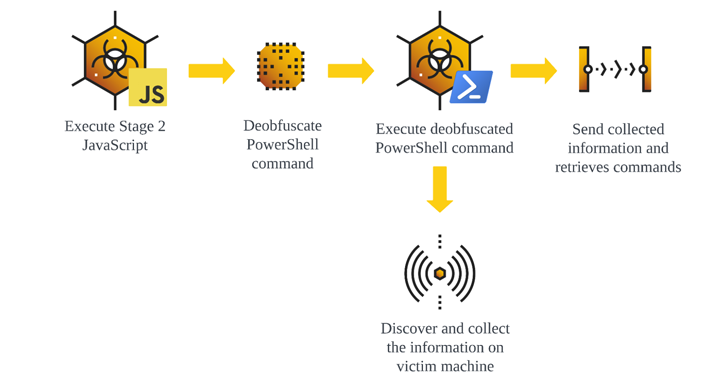
Attack chains involve hacking websites to host the GootLoader JavaScript payload, masquerading as legal documents and agreements that, when run, configure security using a scheduled task and execute additional JavaScript to run a PowerShell script to gather system information and wait for further instructions.

“Sites hosting these archive files use search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning techniques to lure victims looking for business-related files such as contract templates or legal documents,” said security researchers Ralph Villanueva, Kotara Aguina and Gal Romano .
Attacks are also characterized by the use of source code encoding, control flow obfuscation, and payload size enhancements to resist analysis and detection. Another method involves embedding malware into legitimate JavaScript library files such as jQuery, Lodash, Maplace.js, and tui-chart.
“GootLoader has received several updates during its lifecycle, including changes to evasion and execution features,” the researchers concluded.